| Korea: New and Renewable Energy Industry |
 |
| Tuesday, July 21, 2009 |
|
Korea is the world’s 10th largest energy consumer, and has virtually no domestic energy sources of its own. It imports 97% of its energy sources, and is the 6th largest oil importer in the world. To reduce its heavy energy dependency on foreign fossil-fuels, the Republic of Korea Government (ROKG) has launched a series of plans to promote the development and use of new and renewable energies (NRE). The Korean industry has positively responded to the government initiatives by investing in and building more and more power plants using such alternative fuels. Though the Korean Government is making focused investments to address the lack of core technologies and experience in NRE, the Korean power plant industry is constantly seeking imports of advanced technologies, providing ample business opportunities for U.S. NRE companies with innovative technologies.
Korea: New and Renewable Energy Industry. By Young Park, January 09. U.S. Commercial Service. The highlight of ROKG’s policy initiatives towards NRE is Korea’s new National Energy Plan announced in August 2008. Dubbed the “Low Carbon, Green Growth Plan,” it is Korea’s first long-term energy plan proposed to serve as the governing policy for energy generation and use for coming 20 years. According to the Plan, ROKG will increase the ratio of NRE generation out of the entire energy generation from current 2.4% to 11% by 2030. By NRE subsector, specifically; 1) the generation capacity of photovoltaic power will grow from current 80 MW to 3,504 MW (44 times); 2) wind energy will grow from 199 MW to 7,301 MW (37 times); 3) bio energy from 1,874 KGcal to 36,487 KGcal (19 times); 4) and geothermal energy from 110 KGcal to 5,606 KGcal (51 times). |
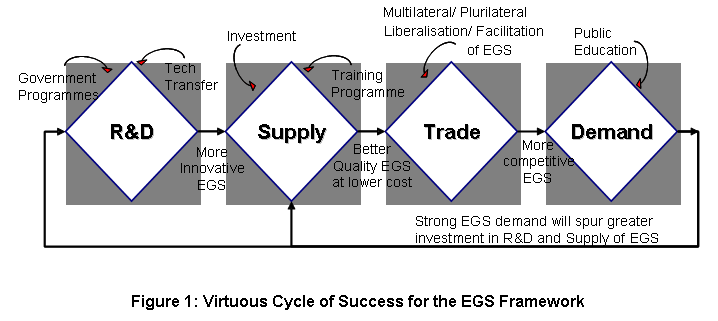 Submitted by Singapore
AIM
This paper seeks CTI's endorsement on a work programme framework for environmental goods and services (EGS) in APEC.
...
Submitted by Singapore
AIM
This paper seeks CTI's endorsement on a work programme framework for environmental goods and services (EGS) in APEC.
...